Wednesday, December 25, 2013
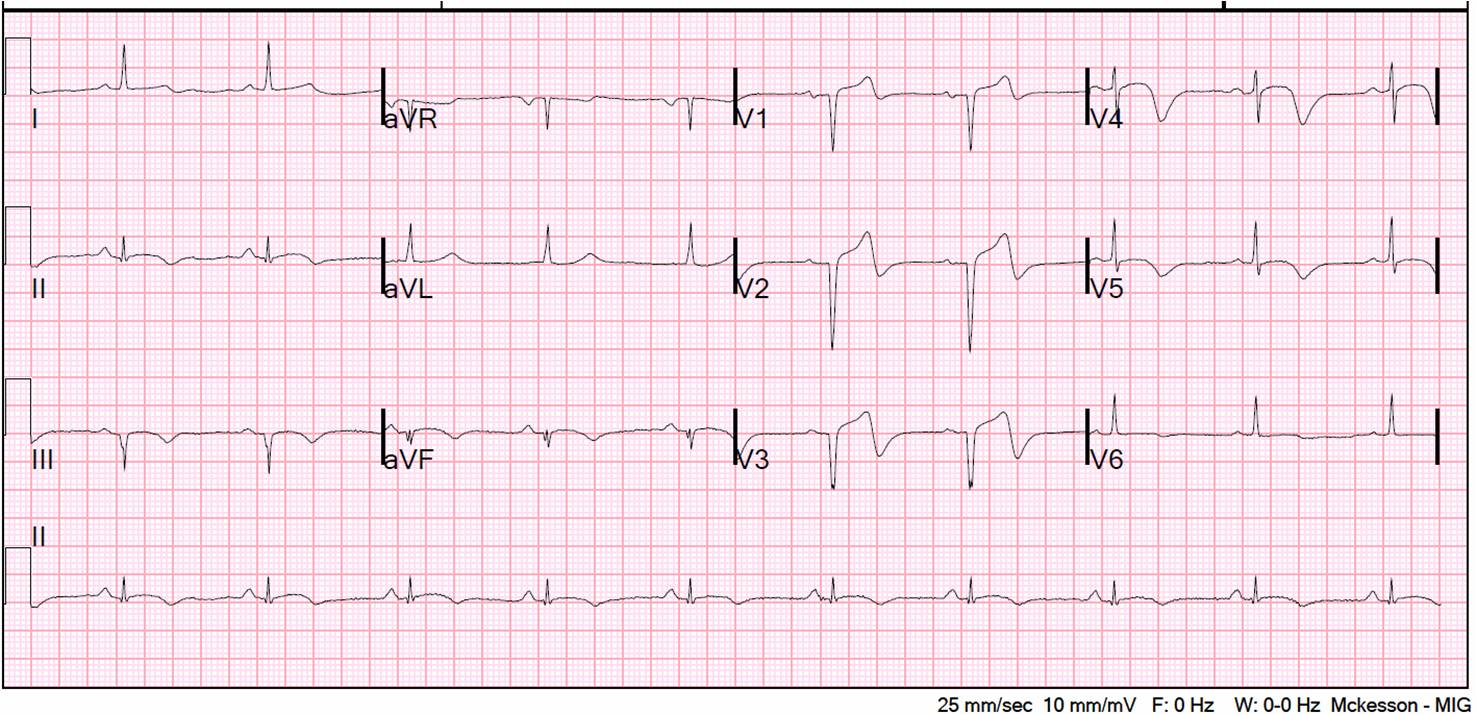
Answer 30
30. Choice A is the correct answer. With right ventricular hypertrophy, there is a large R wave in lead V1. There is a more positive deflection toward the V1 electrode and expect the QRS complex more upright than normal. The S wave in lead V1 is smaller than the R wave. With left ventricular hypertrophy, the left ventricle causes QRS complexes to be bigger in both height and depth in leads V1-V6. There is a larger R wave in lead V5 because it is right over the left ventricle. There is often inversion of the T wave. With atrial hypertrophy there is a biphasic P wave in lead V1. If the initial component is the largest there is right atrial hypertrophy. If the terminal portion of the P wave in lead V1 is the largest, it is left atrial hypertrophy.
Question 30
30. Please identify the abnormality on the EKG listed below:
A. Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
B. Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
C. Left Atrial Hypertrophy
D. Right Atrial Hypertrophy
A. Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
B. Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
C. Left Atrial Hypertrophy
D. Right Atrial Hypertrophy
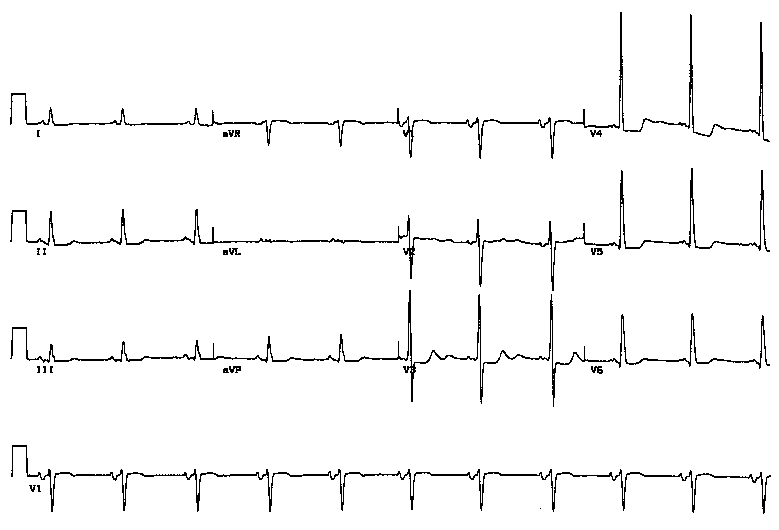
Answer 29
29. Choice D is the correct answer. Hypocalcemia causes prolonged QT interval. This is best assessed in leads V5 and V6. Hypercalcemia causes shortened QT interval. Hypokalemia causes flattened T waves and U waves. Hyperkalemia causes peaked T waves.
Question 29
29. Please identify the abnormality on the EKG listed below:
A. Hyperkalemia
B. Hypokalemia
C. Hypercalcemia
D. Hypocalcemia
A. Hyperkalemia
B. Hypokalemia
C. Hypercalcemia
D. Hypocalcemia
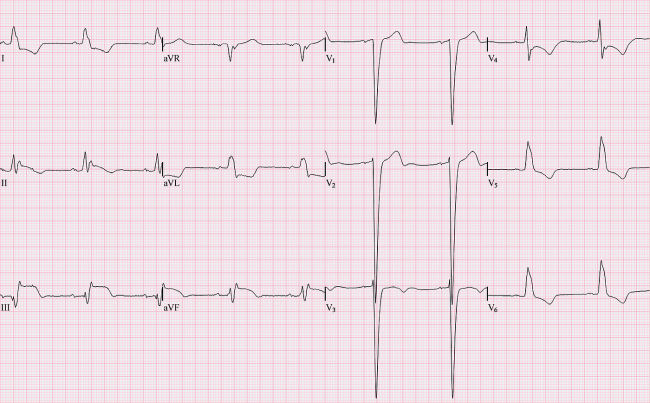
Answer 28
28. Choice B is the correct answer. Left bundle branch block is demonstrated by the R and R' waves in leads V5 and V6. If it is only present in one lead it is referred to as a incomplete left bundle branch block. Hypokalemia is when the T wave is flattened and there may be a U wave present. This is not ventricular tachycardia.
Question 28
28. Please identify the abnormality on the EKG below:
A. Incomplete Left Bundle Branch Block
B. Left Bundle Branch Block
C. Ventricular Tachycardia
D. Hypokalemia
Tuesday, December 24, 2013
Answer 27
27. Choice B is the correct answer. It is a narrow complex tachycardia. It is a rapid sudden onset of a heart rate originating from an ectopic foci form the AV junction. The P wave is inverted and occurring before during or after the QRS complex. Rate is between 150-250 beats per minute. PAT is when the ectopic focus occurs from the atria. Often it is hard to tell if the the P wave is present or not. Collectively these tachycardias are referred to as supraventricular tachycardia. Ventricular tachycardia is a wide complex tachycardia that has a rate over 150 beats per minute. Atrial Fibrillation is an irregularly irregular rhythm that the ectopic focus occurs from the atria.
Question 27
27. Please identify the rhythm in the EKG below:
A. Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia
B. Paroxysmal Junctional Tachycardia
C. Ventricular Tachycardia
D. Atrial Fibrillation
A. Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia
B. Paroxysmal Junctional Tachycardia
C. Ventricular Tachycardia
D. Atrial Fibrillation
Answer 26
26. Choice D is the correct answer. There is both left ventricular and left atrial hypertrophy. The left atrial hypertrophy is demonstrated by the biphasic P wave seen in V1. Since the terminal portion of the P wave is large and wide, this represents left atrial hypertrophy. Left ventricular hypertrophy is demonstrated by the QRS complex in both height and depth in leads V1-V6, the largest S wave and R wave is lead V5.
Question 26
26. Please identify the abnormality listed on the EKG listed below:
A. Left Atrial Hypertrophy
B. Normal EKG
C. Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
D. Both A and C
A. Left Atrial Hypertrophy
B. Normal EKG
C. Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
D. Both A and C
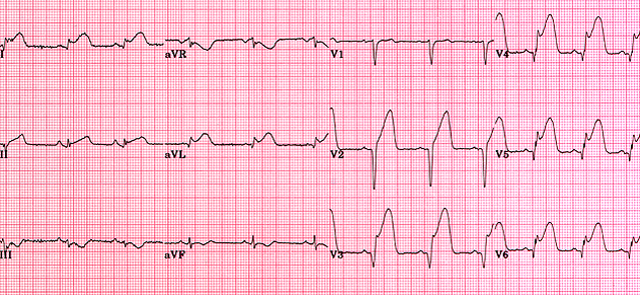
Answer 25
25. Choice A is the correct answer. There is ST elevation in leads V1 and V2 which is consistent with a septal STEMI. There is also some ST elevation in lead V3 which is anterior. There is no ST elevation in the inferior leads (II, III, and avF) and the lateral leads (I, avL, V5 and V6). With a posterior wall MI there is ST depression in leads V1 and V2.
Question 25
25. Please identify the abnormality in the EKG listed below:
A. Septal STEMI
B. Inferior STEMI
C. Posterior STEMI
D. Lateral STEMI
A. Septal STEMI
B. Inferior STEMI
C. Posterior STEMI
D. Lateral STEMI
Answer 24
24. Choice B is the correct answer. With right axis deviation, there is negative deflection of the QRS complex in lead I, and a positive deflection of the QRS complex in lead avF. Extreme right axis deviation has negative deflection in leads I and avF. With left axis deviation there is a positive deflection of the QRS complex in lead I and a negative deflection in lead avF.
Question 24
24. Please identify the abnormality on the EKG listed below:
A. Normal Axis
B. Left Axis Deviation
C. Right Axis Deviation
D. Extreme Right Axis Deviation
A. Normal Axis
B. Left Axis Deviation
C. Right Axis Deviation
D. Extreme Right Axis Deviation
Answer 23
23. Choice B is the correct answer. A PJC originates from an ectopic focus in the AV junction which fires before the normal cycle. PJC's usually are inverted P waves occurring before, during, or immediately after the QRS complex. Premature Ventricular Contractions show a widened QRS complex occurring very early before a P wave. Premature atrial contractions are P waves that occur much normal than usual on an EKG
Question 23
23. Please identify the arrhythmia in the EKG strip below?
A. Premature Atrial Contraction
B. Premature Junctional Contraction
C. Premature Ventricular Contraction
D. Sinus Arrhythmia
A. Premature Atrial Contraction
B. Premature Junctional Contraction
C. Premature Ventricular Contraction
D. Sinus Arrhythmia
Answer 22
22. Choice B is the correct answer. The R and R' waves seen in only V1 and normal R wave in V2 makes it an incomplete right bundle branch block. If the R and R' wave are present in leads V1 and V2 its a complete right bundle branch block. With left bundle branch blocks, the R and R' waves are seen in leads V5 and V6. It is an incomplete left bundle if it is only seen in one of the leads.
Question 22
22. Please identify the pathology in the EKG listed below:
A. Right Bundle Branch Block
B. Incomplete Right Bundle Branch Block
C. Left Bundle Branch Block
D. Incomplete Left Bundle Branch Block
A. Right Bundle Branch Block
B. Incomplete Right Bundle Branch Block
C. Left Bundle Branch Block
D. Incomplete Left Bundle Branch Block
Answer 21
21. Choice B is the correct answer. There is ST elevation in the anteriolateral leads consistent with a STEMI. The patient does have reciprocal changes inferiorly. The patient does not have an inferior STEMI because he has ST depression not elevation in most of those leads. Pericarditis would have diffuse ST elevation throughout all the leads.
Question 21
21. What is the diagnosis on the EKG listed below?
A. Anteriolateral ischemia
B. Anteriolateral STEMI
C. Pericarditis
D. Inferior STEMI
A. Anteriolateral ischemia
B. Anteriolateral STEMI
C. Pericarditis
D. Inferior STEMI
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)